Formulator & Manufacturer
of technical cleaning solvents
for resin manufacturers and applicators
and composite resins
Alternative solvents & substitutes
for ketones, chlorinated solvents,
NMP, NEP and other CMR
__________________________________________________
Polyesters Resins
__________________________________________________
Polyesters resins are widely used according to their utilisation and their implementation.
The UP or UPR unsaturated polyesters are used in several families, the most common of which are:
Aliphatic homopolymers PGA PLA PGL PCL PHA PHB
Co aliphatic polyesters PEA PBS
Semi fragrant co polyesters FBT PTT PEN (PET and PEC saturated thermoplastics)
Homo and Co aromatic polyesters Polyacrylates
Vynilesters resins which are sometimes called "polyester-epoxy hybrid resins" often have applications identical to those of polyesters.
The application of these resins is very broad:
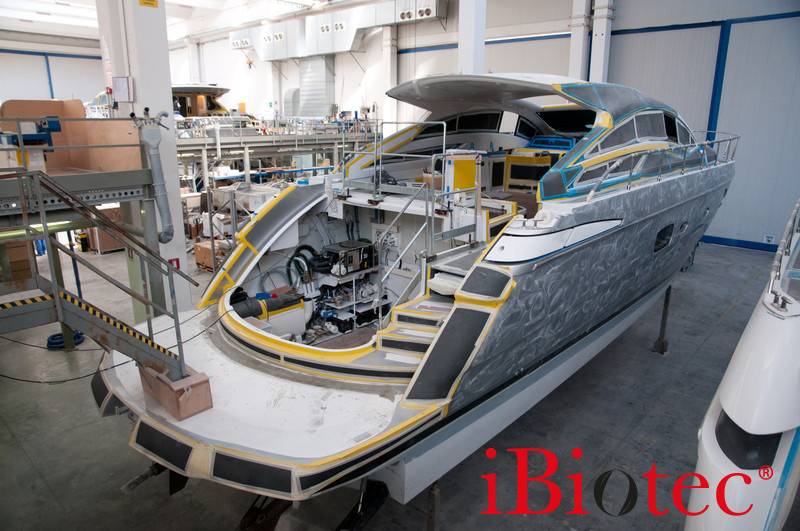
For composites
|
|
|
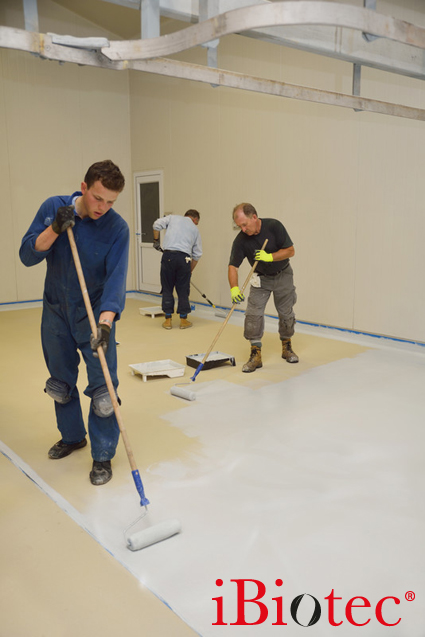
For coating
|
|
|
Note: If the European Directive relating to Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) has been challenged by its applicability, by the industry of fibre reinforced plastics (FRP Fibre reinforced Plastics) concerning the terminology of the stratification of wood and plastics, (based on styrene emissions: reactive monomer, in which the unsaturated polyester is dissolved, but which copolymerizes with the reactive sites of the chains of the unsaturated polyester to form a three-dimensional solid, which is designated as thermosetting plastic), the regulatory framework for the use of cleaning solvents cannot be disputed.
The criteria and needs related to the use of solvents for cleaning unsaturated polyesters are different if it concerns:
RESIN PRODUCTION UNITS, RESINE MAKERS
Generally, ICPE, concerned by the IED directive, the establishment of a SMP, the limitation of VOC emissions, the management and recycling of industrial waste. The solvents used must have a quick dissolution time when cleaning tanks, reactors, mixers between 2 batches if there is no sequencing, or when purging piping or filling systems. This cleaning must be even more horough, when the manufacturing of a hardener follows that of a resin, in the same shift.
Solvents types n methyl pyrrolidone (NMP), n ethyl pyrrolidone (NEP) and gamma butyrolactone (BLO), give good results but are classified CMR (carcinogenic, mutagen, reprotoxic).
IMPLEMENTATION UNITS or WORKSHOPS, APPLICATORS, USERS,
of polyester resins, Applicators, Users
In this case, acetone is very often used. Contrary to the needs of producers, the implementation requires the mixing of a resin and a hardener. The operational cleaning time must be the same as the TECAM hardening time (duration of use of the mixture).
__________________________________________________
Resins Epoxies
__________________________________________________
Epoxy resins fall into the family of thermosetting polymers and find many applications:
Their synthesis was originally designed for usage as structural glue
Common applications
|
|
|
The most common resins are Epichlorohydrin (ECH). Bisphenols A (BPA) suspected of being endocrine disruptors (DGESA) can be replaced by aliphatic or aromatic glycols, phenol novolak or o cresol, hydantoins (glycol-urea), bromine and acrylates.
The most common hardeners are polyisocyanate (diphenyl methane di-isol cyanates DDM - MDA), aliphatic amines, anhydrous hardeners, and TGIC (triglycidyl isocyanurate)
__________________________________________________
Polyurethane resins
__________________________________________________
Polyurethane resins are also called carbamate resins.
This family includes all compounds produced by the reaction of an isocyanate and an alcohol: short or long chain diols or polyols.
They can be obtained by polycondensation or by polyaddition.
Polyurethanes can have many advantages on a technical level, depending on their mode of implementation and their applications, either at low or high pressure.
Low pressure
|
Very good tensile strength, very good dimensional stability under heat, very good resistance to mineral oils in the case of polyester-based polyols, very good resistance to hydrolysis, better flexibility in the cold, resistance to microorganisms in the case of polyether-based polyols. TPUs (thermoplastic elastomers) also have excellent resistance to wear and abrasion, traction and tear, good damping capacity, and excellent resistance to oxygen and ozone. The physical properties of these elastomers and especially their modulus of elasticity, their creep and abrasion behaviour, and their Vicat point (VST), allows them to find many applications. |
|
|
In the form of expanded foam, polyurethane foams are very widely used for their exceptional quality of thermal insulation, their adhesion, their flotation power, and their capacity to fill voids in simultaneous projection. The main uses of flexible or rigid polyurethanes are: Rigid foams for building insulation, household appliances, Flexible moulded or block foams, Elastomers, binders, waterproofing, soleplates, The polyurethane resins can also be used by filament winding, by SMC, BMC, by infusion; they can be thermoformed or machined. From an environmental point of view, they are above all without VOC emission and more particularly without styrene emission (see chapter polyester resins) |
|
__________________________________________________
Choosing solvents - Defining needs
__________________________________________________
Solutions for cleaning solvents and dissolving resins depend on several factors; the choice is more complex when it comes to applicators.
This choice will depend on the time available before total polymerization and obtaining a polymer after the end of polymerization.
This time is defined in 5 steps
1- The storage temperature of the components, or that during application is very low and is insufficient for the reaction to take place.
2- POT LIFE: the temperature of the component(s) is sufficient, the reaction starts.
The pot life is the time after which the viscosity of the mixture doubles.
For example: if the viscosity of the mixture is 10,000 Cps, and it is 20,000 Cps after 30’, then the pot life is 30’.
3- The possible usage time (WORKING LIFE). In general, this value is provided by the manufacturer. This is the time during which the product can be applied.
4- Curing time (GEL TIME TECAM). The product becomes solid, it is no longer applicable (the viscosity can no longer be measured). The polyepoxide formed hardens; we often talk about pre-polymerization.
5- The polyepoxide is fully polymerized, this is the POLYMERIZATION TIME; it has its final physicochemical and mechanical characteristics.
The difficulty can be due to 2 reasons:
At what stage of the reaction do you want to clean? (including dissolving after complete polymerization).
What quantities are used? The times vary according to the quantities: example using 3 grams will not have the same reaction times as using 300 grams for a 5-minute two-component adhesive.
__________________________________________________
Acetone: Danger and toxicity
__________________________________________________
Acetone, if stored or used in excess of 1 tonne enters the SEVESO III domain and is subject to a declaration or to an authorization request to the DREAL (Inspection of classified establishments). The regulatory obligations therefore follow the IED directive for the establishment of a SMP (solvent management plan).
Acetone, apart from its highly flammable character CAT 2, is not toxic safe.
Refer to INRS Toxico sheet N ° 3 Acetone Case 67 641 revision April 2016
- Highly flammable Cat 2 flash point -18°C closed vessel
- Irritant, irritation of the skin and mucous membranes, Serious eye damage Cat 2
- In case of high exposure, breakdown of the nervous system
- Neurological effects, headache, dizziness, comas in certain convulsive cases
- Digestive effects, nausea, vomiting, hematemesis
- Specific toxicity for target organ
- Cat 3 narcotic effects
- Article 4412-149 of the VLEP labour code
VLE RESTRICTION VME 500 ppm VLCT 1000 ppm